Question
DaVinci Resolveでデリバー(エクスポート)した動画をYouTubeにアップロードしましたが、音量が小さかったり、音割れがしたりします。アップロード前のファイルを再生しても十分な音量があります。YouTube用の動画として適切な音の調整方法はありますか?
Answer
YouTubeなどを拝見すると、個人がアップロードされている 作品に限らず、プロのアーティストがアップロードされているものでも同様の問題を目にする(耳にする?)ことがあります。
理由
ラウドネスの考え方とそれによって起きる不都合
YouTubeなどのWebサービスの仕様
YouTubeなどのWebサービスの音量制限
YouTube 上で問題を数値で確認する方法
DaVinci Resolveでできる対策
理由、問題を数値で確認する方法、対策は 次の通りです。
理由
3つの原因で発生します。
なお、専門的な用語を極力使わず、わかりやすい言葉で書いていますが、表現の修正が望ましい箇所がありましたら、ご指摘ください。
ラウドネスの考え方とそれによって起きる不都合
テレビなどのサービスで複数の作品(番組やCM、他のチャンネル)を連続して視聴しても程よくボリュームが揃うことを目的として生まれた考えた方です。ラウドネスの考え方の前に、最大音量に関する考え方もありましたが、それでは常に最大音量付近の音ばかりを使う問題もあったので、ラウドネスは生まれました。
ラウドネスは作品内の音量の平均を表すもので、最大音量を示すものではありません。
小さい音と大音量の組み合わせでは、ラウドネスでは問題なくても、小さな音が小さすぎるといったことが不都合も起きえます。
また、ラウドネスを守っていても音量が大きく聞こえるなどはありえます。これは人の耳の特性も関係しています。
参考: ラウドネスを守っていても RモバイルのCMが極端に大きく感じた件をしっかりと考察されています。
YouTubeなどのWebサービスの仕様
YouTubeなどのWebサービスの仕様により、音量が下げられる場合があり、結果として、音割れや音の痩せが発生します。
動画や音声を扱うWebサービスの多くは、他の作品との音量を一定にするために、音量を制限しています。ただし、制限以下の場合に音量を引き上げるような処理はしません。これにより、アップロードした作品により、次のような状況となります。
- 音量が制限より大きい場合
他の作品に合わせた音量に下がる
→他の作品と音量は揃うが、想定していたものより小さい、音割れや音が痩せる - 音量が制限より小さい場合
アップロードの音量のまま
→他の作品よりも小さいまま
YouTubeなどのWebサービスの音量制限
Webサービス 毎に扱う音量制限には、ばらつきがあります。また、公式にその制限を公開している場合もありますが、YouTubeのように公開されていないサービスも存在します。
単位としての意味は異なりますが、今回のような動画での話であれば、LUFSはdBと読み替えていただいて問題ありません。
テレビ -23LUFS ~ -25LUFS
ニコニコ動画 -15 LUFS
YouTube -13LUFSもしくは-14LUFS (情報非公開)
YouTubeは非公開のため、様々な方が調査しています。時期などにもよるかと思いますが、私が調べた限りでは-14 LUFS と考えています。
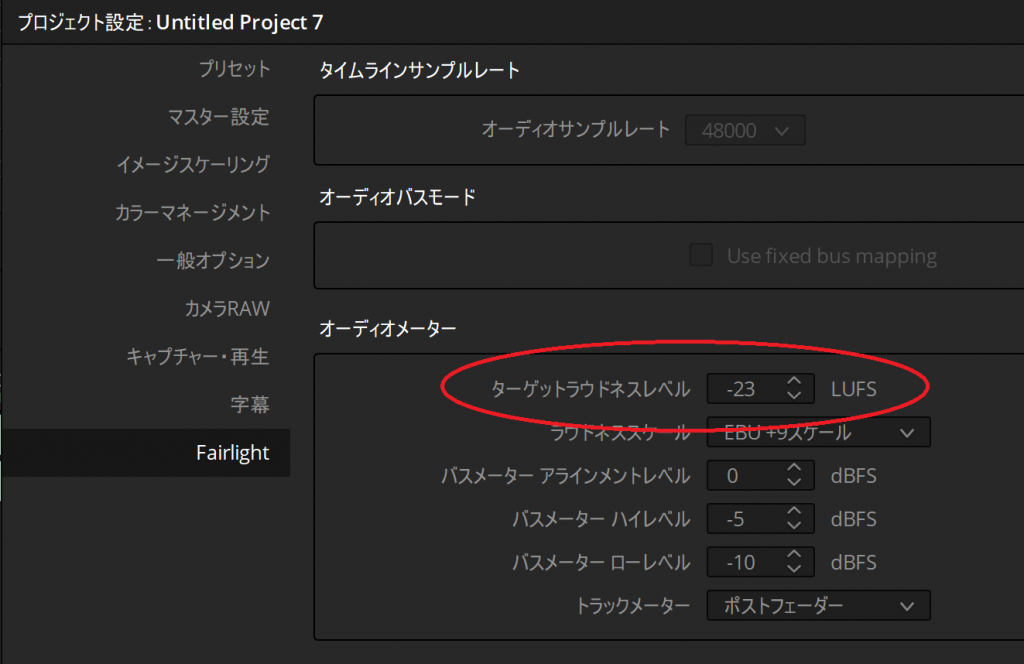
なお、後述しますが、DaVinci Resolve上には編集時のラウドネスのターゲットを決める設定がありますが、それは「-23LUFS」がデフォルトに設定されています。(テレビがデフォルトになっているのですね。)
サービスが対応する制限以下の音量のデータをアップロードするのが望ましいです。理想は制限ギリギリです。ただ、WEBサービス側は制限以上の場合でも扱えるようにしており、制限以上の音量に対しては、WEBサービス側でボリュームを下げる処理をしています。(WEBで調べた限りでは、Twitterの動画はラウドネスによるボリューム制限はかけていないそうです。(未検証))
YouTube 上で 問題を数値で確認する方法
利用されるWebサービスによって、元データに対してどれだけの音量で公開されているかの確認方法は、サービスによって異なります。
ここでは、最も一般的なYouTubeを例に説明します。
PCのブラウザでYouTubeを開き、該当の動画を再生します。
再生中に動画のウィンドウを右クリックして、「詳細統計情報」を選択します。
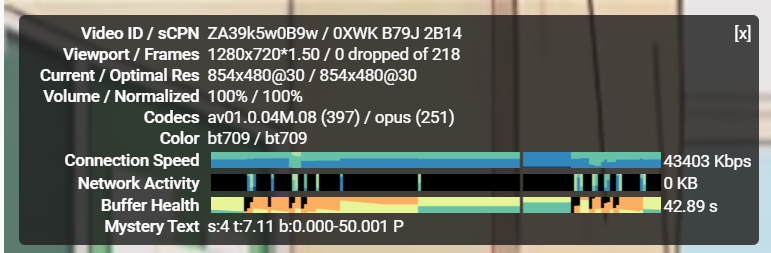
「Volume / Normalizated」の特に「content loundness」に注目しますが、簡単にその他の値も説明します。
例を挙げて説明します。次の例では、「100% / 56% (content loundness 5.1db)」となっています。
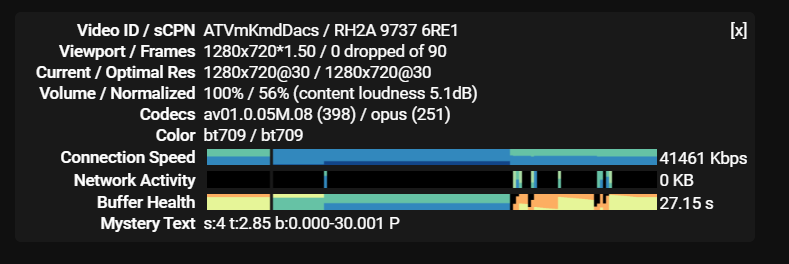
はじめの「100%」は、Youtubeを再生している画面のボリュームの位置です。再生画面左下のボリュームで変化します。最大音量の場合、100%になります。
2つめの「56%」は元のデータに対してどれだけボリュームを下げているかを意味します。この例ではアップロードしたデータから56%になっていることを意味します。ボリュームは「100%」ですので、元データとしては56%になるように音量が下げられていることがわかります。また、Youtubeの画面のボリュームを変更すると、この例で「56%」となっている値はが変わる事も確認できます。
3つめの「content loundness 5.1dB」は、 元のデータに対して、5.1dB下げた状態で配信されていることを意味します。「2.」のような画面の ボリュームとは関係なく、常にこの値だけは下げた状態で再生されるという意味です。
このように元の音量がYouTubeの制限よりも大きい場合は、音量を下げて提供されることになります。この音量を下げる処理の中により、 想定していたものより小さい、音割れや音が痩せるといった状況になります。
また、次の例では 「-14.9dB」ですので、元データが14.9dBも音量が低い ことを意味します。
注目点としては、 Volume とNormalizated の値が一致しています。これは、元データの音量が低いにも関わらず、配信時のボリュームは上げて配信していないことを意味しています。これは、「音量が制限より小さい場合 」に記載した仕様の通りです。言い換えると、14.9dB 分の音量・音質を損していると見ることができます。
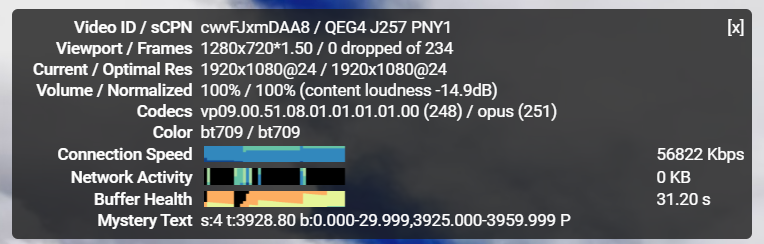
次のものは珍しくピッタリです。これがベストと言えますが、非常に珍しいです。(初めて目にしました。)
DaVinci Resolveでできる対策
対策は現在作成中です。
次の動画が参考になるので、そちらを確認ください。
音量の大きい音を抑える方法 コンプレッサーとリミッター
//////////////以下作成中/////////////////////////
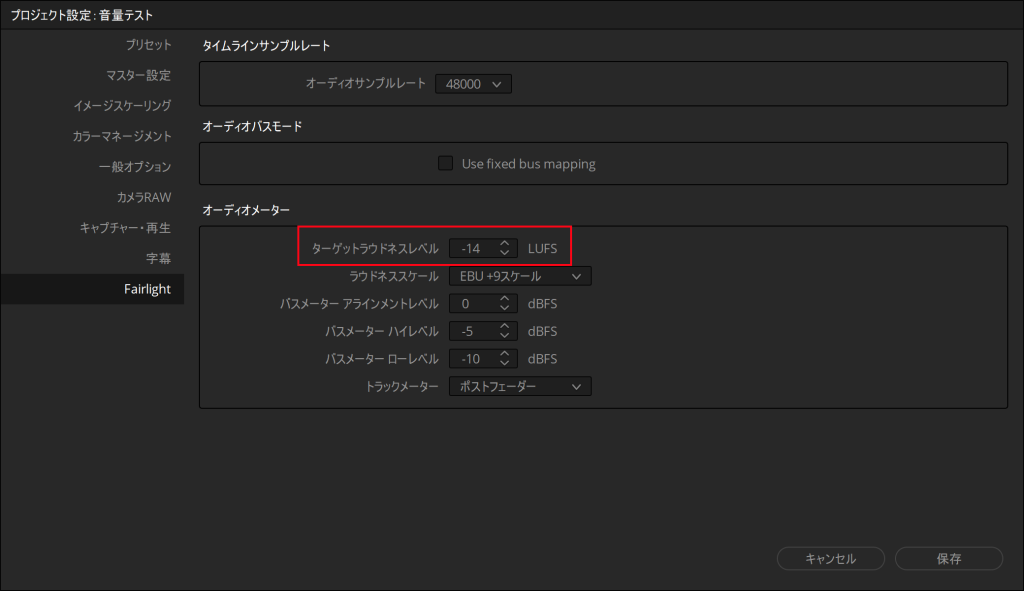
プロジェクト設定の「Fairlight」にある「オーディオメーター」の「ターゲットラウドネスレベル」を「‐14」に設定。(デフォルトでは「‐23」)
アップロードした結果、「content loundness」が「-3dB~0」程度にするように動画を作成するのが望ましいです。なお、DaVinci Resolveを含め、編集ソフト上でラウドネスが0であっても、アップロード先で多少音量を下げられる場合があります。多少下げられても大きな劣化はないですが、一度、音量の最小・最大の箇所だけでも確認されることをお勧めます。
ノーマライズ
Fairlight上で書き出す範囲のオーディオレベルをノーマライズします。
該当するオーディオをすべて選択して、右クリックから「オーディオレベルをノーマライズ」を選択
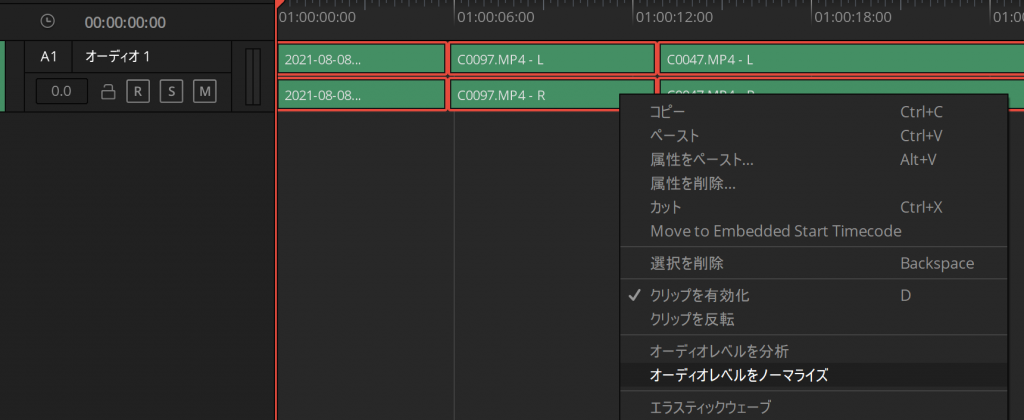
ノーマライズモードを「ITU-R BS.1770-4」を選択し、
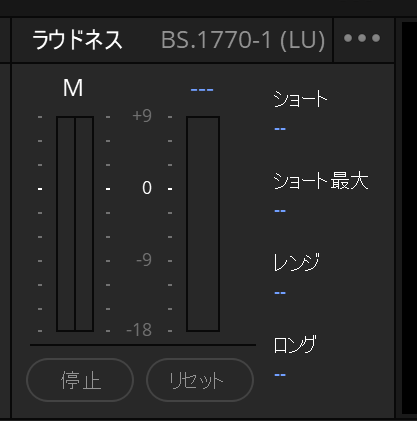
ラウドネスメーターで確認します。再生した間のラウドネスを数値で表示します。
音量の大小の差が大きい場合
音量の大小の差が大きい場合 、ラウドネスは平均値で評価するため、小さな音が小さすぎる結果になる場合があります。
小さな音の場所に対して音量を上げる調整する、もしくは、 大きな音の場所に対して音量を下げる調整する必要があります。
また、先の通り全体の平均値であるため、あくまで目安。必ずしも、ラウドネスの値を死守する必要なないです。
当然ながら、人の耳の周波数特性に合わせて、特定の周波数帯だけを上げることで対処することもできますが、熟練が必要かもしれません。


